How to Prepare for the AZ-303 Exam?
Preparing for the AZ-303 Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies exam? Don't know where to start? This post is the AZ-303 Study Guide, which helps you to achieve the Microsoft Azure Certified Solutions Architect expert certification.
Note: You also need to clear AZ-304 to achieve this certification.
This post contains a curated list of articles from Microsoft documentation for each objective of the AZ-303 exam. Please share the post within your circles so it helps them to prepare for the exam.
Exam Voucher for AZ-303 with 1 Retake
Get 40% OFF with the combo
AZ-303 Microsoft Azure Architect Online Course
AZ-303 Microsoft Azure Architect Practice Test
AZ-303 Azure Architect Other Training Materials
AZ-303 Sample Practice Exam Questions

Looking for AZ-303 Dumps? Read This!
Using az-303 exam dumps can get you permanently banned from taking any future Microsoft certificate exam. Read the FAQ page for more information. However, I strongly suggest you validate your understanding with practice questions.
Check out all the other Azure certificate study guides
Full Disclosure: Some of the links in this post are affiliate links. I receive a commission when you purchase through them.
Implement and Monitor an Azure Infrastructure (50-55%)
Implement Cloud Infrastructure Monitoring
Monitor security
Visualize and monitor your data
What is Azure Security Center?
What is Azure Sentinel?
Monitor performance
Monitor health and availability
Monitor cost
Configure advanced logging
Configure and manage advanced alerts

Implement Storage Accounts
Select storage account options based on a use case
Introduction to the core Azure Storage services
Configure Azure Files and blob storage
Create an Azure file share
Configure network access to the storage account
Configure Azure Storage firewalls & virtual networks
Implement Shared Access Signatures and access policies
Grant limited access to Azure Storage resources using SAS
Define a stored access policy
Implement Azure AD authentication for storage
Azure Active Directory (AD) based access control
Authorize access to blobs & queues using Azure AD
Manage access keys
Manage storage account access keys
Implement Azure storage replication
The explanation for Azure storage replication
Implement Azure storage account failover
Disaster recovery & storage account failover
Initiate a storage account failover
Implement VMs for Windows and Linux
Configure High Availability
Create & deploy highly available VMs with Azure PowerShell
Configure storage for VMs
Introduction to Azure managed disks
Select virtual machine size
Sizes for virtual machines in Azure
Implement Azure Dedicated Hosts
Deploy VMs to dedicated hosts using the portal
Deploy and configure scale sets
Creating VM scale sets in the Azure portal
Configure Azure Disk Encryption
Create & encrypt a Windows VM with the Azure portal
Automate Deployment and Configuration of Resources
Save a deployment as an Azure Resource Manager template
Download the template for a VM
Modify Azure Resource Manager template
Updating resources in an Azure Resource Manager template
Evaluate the location of new resources
Set resource location in the ARM template
Configure a VHD template
Deploy Azure virtual machines from VHD templates
Deploy from a template
Create a Windows VM from a Resource Manager template
Manage an image library
Shared Image Galleries
Create an Azure Shared Image Gallery
Create and execute an automation runbook
Deploy an ARM template in a PowerShell runbook
Implement Virtual Networking
Implement VNet to VNet connections
VNet-to-VNet VPN gateway connection using PowerShell
Implement VNet peering
YouTube video: VNet Peering demo

Amazon link (affiliate)
Implement Azure Active Directory
Add custom domains
Add your custom domain name using the Azure AD portal
Configure Azure AD Identity Protection
Configure notifications in Azure AD Identity Protection
Configure the Azure MFA registration policy
Implement self-service password reset
Using Azure AD self-service password reset
Implement Conditional Access including MFA
Conditional Access: MFA for all users
Configure fraud alerts
Fraud alert feature
Configure verification methods
Verification methods in Azure MFA
Implement and manage guest accounts
Add guest users to your directory in the Azure portal
Manage guest access with Azure AD access reviews
Manage multiple directories
Understand how multiple Azure AD organizations interact
Implement and Manage Hybrid Identities
Install and configure Azure AD Connect
Getting started with Azure AD Connect using express settings
Identity synchronization options
Objects and credentials in an Azure AD DS
Configure and manage password sync and password writeback
Implement password hash synchronization with Azure AD Connect sync
Azure Azure AD self-service password reset
Configure single sign-on
Using Azure AD as your Identity & Access Management
Configure Azure AD Connect cloud sync
What is Azure AD Connect cloud sync?
Use Azure AD Connect Health
Azure AD Connect Health: Monitoring the sync engine
Implement Management and Security Solutions (25-30%)
Manage Workloads in Azure
Migrate workloads using Azure Migrate
Implement Azure Backup for Azure workloads
Back up an Azure VM from the VM settings
Implement disaster recovery
Set up disaster recovery for Azure VMs
Implement Azure Automation Update Management
Update Management overview
Enable Update Management from Azure portal
Implement Load Balancing and Network Security
Implement Azure Load Balancer
Load balance internet traffic to VMs using the Azure portal
Implement an Azure application gateway
Using Azure PowerShell to create an application gateway
Implement a Web Application Firewall
Using the Azure portal to create an Application Gateway with a WAF
Implement Azure Firewall
Deploy & configure Azure Firewall using the Azure portal
Implement Azure Firewall Manager
Secure your virtual hub using Azure Firewall Manager
Implement Azure Front Door
Use the Azure Front Door – Redirect HTTP to HTTPS
Implement Azure Traffic Manager
Create a Traffic Manager profile using the Azure portal
Implement Network Security Groups and Application Security Groups
Create, change, or delete a network security group
Application security groups
Implement Bastion
Connect to a VM using a private IP address & Azure Bastion

Implement and Manage Azure Governance Solutions
Create and manage hierarchical structure that contains management groups, subscriptions, and resource groups
Create a management group
Assign RBAC roles
Grant a user access to Azure resources by Azure portal
Create a custom RBAC role
Create an Azure custom role using Azure PowerShell
Configure access to Azure resources by assigning roles
Add a role assignment
Configure management access to Azure
Best practices for Azure RBAC
Interpret effective permissions
View the access a user has to Azure resources
Set up and perform an access review
What are Azure AD access reviews?
Implement and configure an Azure Policy
Create & manage policies to enforce compliance
Implement and configure Azure Blueprints
Working with Azure Blueprints
Manage Security for Applications
Implement and configure Key Vault
Pluralsight course on Azure Key Vault (Free trial)
Implement and configure Managed Identities
Windows VM system-assigned managed identity to access ARM
Register and manage applications in Azure AD
Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform
Implement Solutions for Apps (10-15%)
Implement an Application Infrastructure
Create and configure Azure App Service
Create an ASP.NET Core web app in Azure
Create an App Service Web App for Containers
Run a custom container in Azure
Create and configure an App Service plan
Azure App Service plan overview
Configure an App Service
Configure an App Service app in the Azure portal
Configure networking for an App Service
Integrate your app with an Azure virtual network
Create and manage deployment slots
Set up staging environments in Azure App Service
YouTube video: Deployment slots
Implement Logic Apps
Azure Logic Apps for schedule-based & recurring automation workflows
Implement Azure Functions
Create a function in Azure that's triggered by Blob storage
Implement Container-based Applications
Create a container image
Build & deploy container images in the cloud with ACR Tasks
Configure Azure Kubernetes Service
Deploy an AKS cluster using the Azure portal
Publish and automate image management by using the Azure Container Registry
Private Docker container registry using the Docker CLI
Automate container image builds & maintenance with ACR Tasks
Deploy a solution on an Azure Container Instance
Deploy a container instance in Azure using the Azure portal
Implement and Manage Data Platforms (10-15%)
Implement NoSQL Databases
Configure Azure storage account tables
Create an Azure Storage table in the Azure portal
Create a table dynamically with the .NET SDK (Table API)
Notes:
Don't get confused with the Table API in Cosmos DB and Azure Table storage. They both share the same data model and expose similar query operations through their SDKs.
But, Table API in Cosmos DB has premium capabilities like global distribution, throughput & high availability. So, you should look to migrate your existing app to Table API, given a chance.
Select appropriate CosmosDB APIs
Review the Learning Path: Choose the appropriate API for Azure Cosmos DB
Notes:
Cosmos DB is a Multi-Model Database Service. It means that you can build any of the NoSQL database models with the following APIs:
1. Gremlin (Graph) API – To describe the relationship between entities.
2. Azure Table API – use only to migrate applications using Azure Table Storage to Cosmos DB. Else just avoid.
3. MongoDB API – If your project is already using MongoDB, use this API. Migration is as simple as just updating the connection string.
4. Cassandra API – If your team already uses Cassandra DB / skillful of Cassandra Query Language (CQL), use this API.
5. Core SQL API – For all other cases & for new projects, use SQL API. Superior in functionality to other APIs. When in doubt, use Core SQL.
Set up replicas in CosmosDB
A Pluralsight module on understanding global distribution & replication
Add/remove regions from your Cosmos DB account
Configure Multiple write-regions
Configure Multi-master in your app (To write to the nearest write location)
Notes:
a. Why data replication is important in Azure Cosmos DB?
1. To reduce the latency of your application. If you have a global audience, then the users farther from the database may experience high latency (time duration between request & response). By enabling Cosmos DB replication, you direct the request to the nearest data center. The SDK will make sure of that.
2. Replication enables Business Continuity. If there is a natural disaster in a data center, you know the data is safe elsewhere.
b. In addition, to read replication, you can set up multi-region writes. But why? Same reason! To reduce write latency. But, this may cause conflicts as the data is updated in different regions.
Implement Azure SQL Databases
Configure Azure SQL database settings
Configure Server-level IP firewall rules
Configure security features of Azure SQL Database like:
Notes:
You need to open port 1433 if you try to connect the Azure SQL database from your system (with a client tool like SSMS).
You can create Server-level firewall rules in the Azure portal and T-SQL (with SSMS). Database-level firewall rules can be configured with only T-SQL statements.
Server-level firewall rules apply to all the databases in the server & they are created in the master database. The rules for the database-level firewall are stored in the individual database making them easily portable.
Implement Azure SQL Database managed instances
Getting started with Azure SQL Managed Instance
Creating an Azure SQL Database Managed Instance
Notes:
Best used for migrating existing on-premises applications with minimal effort (lift-and-shift). Provides the latest stable DB engine version.
Azure SQL Managed Instance = Best of Azure SQL Database + Best of SQL Server on Azure VM
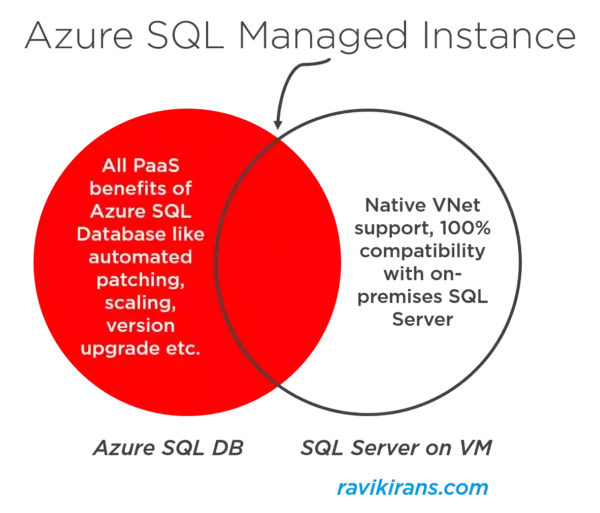
Configure HA for an Azure SQL database
High-availability for Azure SQL Database
Notes:
What High Availability ensures for Azure SQL Database?
- That data is immune to failures.
- SQL, Windows maintenance operations do not impact the workload.
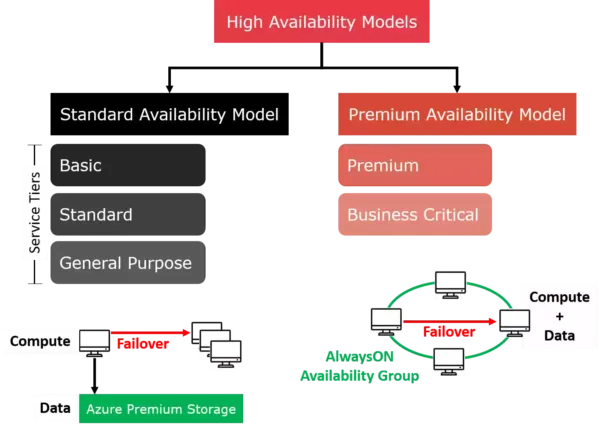
High-availability models available:
Standard: Basic, Standard & General Purpose tiers use the standard model: Two layers – a stateless compute layer & a stateful data layer (the .mdf & .ldf files) stored in Azure premium storage (built-in high availability). In the case of failure, Azure Service Fabric kickstarts another stateless compute node. Not suitable for a heavy workload, as the new compute node does not have any files (cold cache).
Premium (leveraged by Premium & Business Critical service tiers): Unlike the previous model, both the compute and the storage is in the same node. This node is replicated 3-4 times (others are secondary nodes) to provide high availability (implemented with Always On availability groups).
Additional benefits of Premium availability model:
Read Scale-Out: You can redirect read operations to the secondary nodes
Availability Zones: You can place the databases in availability zones so the data is replicated across data centers in a region. Although the data is immune to data center-specific failures, you may observe network latency (due to distance between data centers) as transactions are committed across availability zones.
Deploy an Azure SQL database
Different ways to publish updates to Azure SQL Database
Example: Deploy a data-driven app with App Service & Azure SQL Database
This brings us to the end of the AZ-303 Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies Study Guide
What do you think? Let me know in the comments section if I have missed out on anything. Also, I love to hear from you about how your preparation is going on!
In case you are preparing for other Azure certification exams, check out the Azure study guide for those exams.
Follow Me to Receive Updates on AZ-303 Exam
Want to be notified as soon as I post?Subscribe to the RSS feed / leave your email address in the subscribe section.Share the article to your social networks with the below links so it can benefit others.
Share the AZ-303 Study Guide in Your Network
Source: https://ravikirans.com/az-303-azure-exam-study-guide/
Posted by: jeraldjeraldbocagee0269153.blogspot.com